In today’s fast-paced software industry, delivering applications quickly, reliably, and efficiently is critical. DevOps automation has emerged as a key strategy for streamlining software deployment, reducing errors, and improving collaboration between development and operations teams. By automating repetitive tasks, organizations can accelerate release cycles, increase stability, and focus on innovation rather than manual processes.
This article explores how DevOps automation enhances software deployment, its key benefits, tools used, and best practices for implementation.
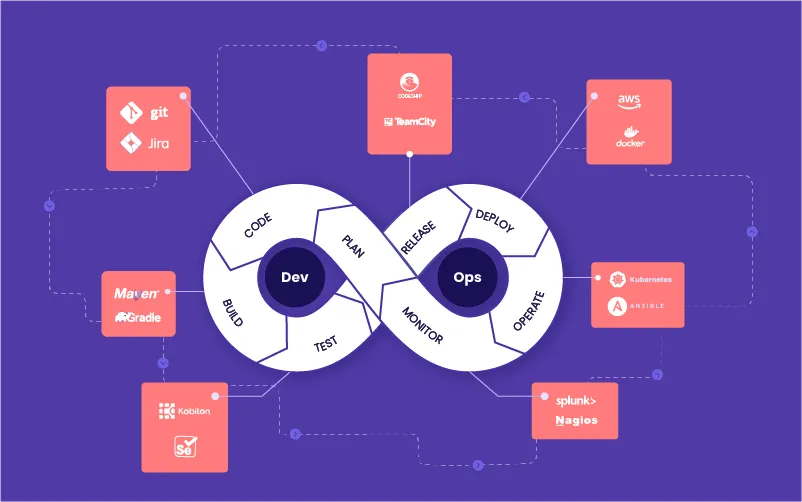
What is DevOps Automation?
DevOps is a cultural and technical approach that unites software development (Dev) and IT operations (Ops) to improve collaboration and delivery. Automation in DevOps refers to the use of tools and scripts to handle repetitive, time-consuming tasks such as:
-
Code integration and testing
-
Application builds and deployments
-
Infrastructure provisioning
-
Monitoring and logging
By automating these processes, DevOps reduces human error, speeds up deployment cycles, and ensures consistent outcomes across environments.
Key Benefits of DevOps Automation in Software Deployment
1. Faster Deployment Cycles
Automated pipelines allow continuous integration and continuous delivery (CI/CD), enabling teams to deploy new features or bug fixes rapidly without manual intervention. This reduces time-to-market and keeps organizations competitive.
2. Reduced Human Error
Manual deployment processes are prone to mistakes, such as incorrect configurations or missing dependencies. Automation ensures standardized, repeatable procedures, minimizing errors and improving reliability.
3. Enhanced Collaboration
Automation bridges the gap between development and operations teams. Shared pipelines, version control, and automated testing create transparency, improving teamwork and reducing deployment friction.
4. Scalability and Flexibility
Automated deployments make scaling applications easier. Teams can deploy updates across multiple servers, cloud environments, or regions with minimal effort, supporting modern infrastructure requirements.
5. Efficient Resource Utilization
By automating repetitive tasks, teams can focus on high-value activities such as innovation, security, and optimization. This improves productivity and reduces operational overhead. Additionally, automation contributes indirectly to sustainability initiatives, complementing efforts like Green Computing Technologies Reducing Carbon Footprint by optimizing resource usage.
Common DevOps Automation Tools
| Tool | Purpose | Key Features |
|---|---|---|
| Jenkins | CI/CD pipeline automation | Builds, tests, and deploys applications automatically |
| Ansible | Configuration management | Automates server provisioning, app deployment, and updates |
| Docker | Containerization | Ensures consistent environment across deployments |
| Kubernetes | Container orchestration | Automates scaling, deployment, and management of containers |
| GitLab CI/CD | Integrated DevOps | Manages code, pipelines, testing, and deployments in one platform |
| Terraform | Infrastructure as code | Automates provisioning and management of cloud infrastructure |
These tools work together to create robust, repeatable, and reliable software deployment processes.
Best Practices for Implementing DevOps Automation
-
Start Small: Begin with automating the most repetitive tasks and gradually expand.
-
Adopt CI/CD: Continuous integration and delivery pipelines ensure faster, safer deployments.
-
Use Infrastructure as Code: Manage infrastructure through code to improve consistency and scalability.
-
Integrate Automated Testing: Catch bugs early by automating unit, integration, and regression tests.
-
Monitor and Optimize: Continuously track deployment metrics and refine pipelines for efficiency.
-
Foster a Collaborative Culture: Encourage communication between development, operations, and QA teams.
Following these best practices ensures a smooth adoption of automation and maximizes the benefits for deployment processes.
Challenges and Considerations
While DevOps automation offers numerous advantages, teams may face challenges such as:
-
Initial setup complexity and cost
-
Requirement for skilled personnel
-
Integration with legacy systems
-
Continuous monitoring to prevent pipeline failures
Careful planning and phased implementation help mitigate these challenges and ensure a successful automation strategy.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the difference between DevOps and DevOps automation?
DevOps is the overall cultural and operational approach, while automation specifically refers to using tools and scripts to streamline tasks.
Can automation replace human involvement entirely?
No, human oversight is still needed for decision-making, monitoring, and handling complex scenarios.
How long does it take to implement DevOps automation?
It depends on the organization’s size, complexity, and existing infrastructure; small initiatives can take weeks, while full adoption may take months.
Is DevOps automation suitable for small teams?
Yes, automation can help small teams reduce manual workload and improve deployment consistency.
Does automation improve software quality?
Yes, automated testing and standardized deployments reduce errors, improve reliability, and maintain consistent performance.
Conclusion
DevOps automation significantly improves software deployment by accelerating release cycles, reducing errors, enhancing collaboration, and optimizing resource usage. By leveraging tools like Jenkins, Ansible, Docker, and Kubernetes, organizations can create efficient, scalable, and repeatable deployment pipelines.
Automation not only streamlines technical processes but also contributes indirectly to sustainability and efficiency, complementing initiatives such as Green Computing Technologies Reducing Carbon Footprint. Implementing DevOps automation strategically allows organizations to deliver high-quality software faster, with greater reliability and adaptability, keeping them competitive in the modern software landscape.