The world of work is undergoing a dramatic transformation driven by artificial intelligence (AI) and automation technologies. From routine administrative tasks to complex decision-making processes, AI and automation are reshaping how businesses operate, how employees engage with their work, and the skills required for the modern workforce.
This article explores the future of work in an AI-driven world, the benefits and challenges of automation, and strategies for individuals and organizations to thrive in this evolving landscape.
How AI and Automation Are Changing the Workplace
AI and automation technologies are increasingly embedded in everyday business operations, transforming traditional work models in several key ways:
-
Task Automation: AI handles repetitive tasks like data entry, scheduling, and basic customer queries, freeing human workers for higher-value activities.
-
Enhanced Decision-Making: Machine learning algorithms analyze vast datasets to inform strategic decisions faster and more accurately.
-
Intelligent Collaboration: AI-powered tools enable smarter team collaboration, predictive project management, and workflow optimization.
-
Personalized Employee Experience: Automation and AI can customize learning, performance tracking, and work schedules for employees.
-
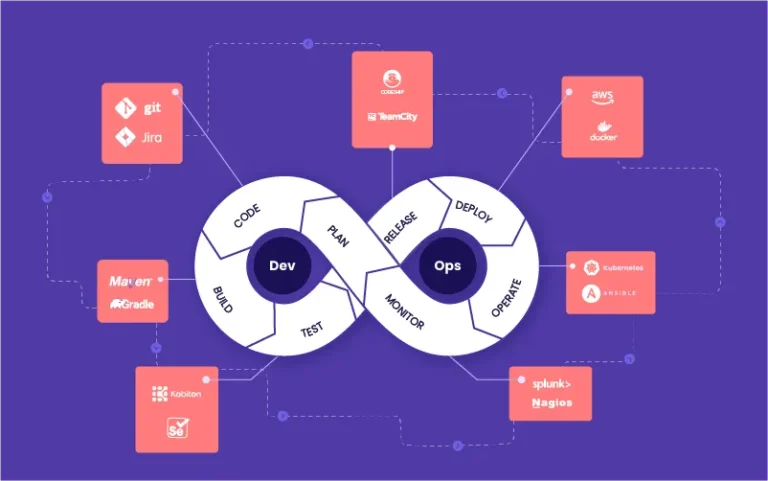
Innovation Enablement: By automating routine processes, organizations can redirect resources to innovation and creative problem-solving, similar to the efficiency gains seen in How DevOps Automation Improves Software Deployment.
Key Benefits of AI and Automation in the Workplace
1. Increased Productivity
Automation of repetitive tasks allows employees to focus on creative and strategic work, improving overall productivity.
2. Accuracy and Consistency
AI reduces human errors in data processing, reporting, and operational tasks, ensuring consistent outcomes.
3. Cost Efficiency
Automated systems reduce labor costs, minimize errors, and optimize resource allocation, leading to better financial efficiency.
4. Scalability
AI solutions enable organizations to scale operations rapidly without proportional increases in workforce size.
5. Improved Employee Satisfaction
Removing monotonous tasks increases job satisfaction and allows employees to focus on meaningful, engaging work.
Examples of AI and Automation in Work Environments
| Area | AI/Automation Application | Benefits |
|---|---|---|
| Customer Service | Chatbots and virtual assistants | 24/7 support, faster response times |
| Finance | Automated invoice processing | Reduces errors, speeds up transactions |
| HR | AI-powered recruitment tools | Identifies best candidates quickly |
| Marketing | Predictive analytics | Personalizes campaigns, improves ROI |
| Operations | Workflow automation | Increases efficiency and reduces bottlenecks |
| Manufacturing | Robotics and AI-controlled machinery | Enhances precision, reduces downtime |
These examples highlight how AI and automation are transforming various sectors, from knowledge work to industrial processes.
Challenges of AI and Automation
Despite the benefits, the integration of AI into the workplace comes with challenges:
-
Job Displacement: Certain roles may become obsolete, requiring workforce reskilling.
-
Ethical Considerations: AI decision-making must be transparent and unbiased.
-
Data Privacy: Automation relies on data, creating privacy and security concerns.
-
Dependence on Technology: Overreliance may reduce human judgment in critical situations.
-
Skill Gaps: Employees need to develop digital literacy, critical thinking, and AI fluency to thrive.
Organizations must address these challenges through responsible AI adoption, ethical guidelines, and continuous training programs.
Preparing for the AI-Driven Future of Work
1. Invest in Upskilling
Employees must learn new skills in AI, data analytics, programming, and digital collaboration tools to stay competitive.
2. Foster Human-AI Collaboration
Rather than replacing humans, AI should complement human capabilities, allowing employees to focus on creativity, empathy, and critical thinking.
3. Redesign Jobs and Processes
Evaluate workflows and redesign roles to incorporate automation effectively while ensuring meaningful human engagement.
4. Embrace Agile Work Cultures
Organizations should adopt agile structures to respond quickly to technological changes and evolving business demands.
5. Ethical and Responsible AI Use
Establish guidelines to ensure AI and automation are implemented transparently, fairly, and securely.
Frequently Asked Questions
Will AI completely replace human jobs?
AI will automate certain tasks, but most roles will evolve rather than disappear, requiring reskilling and adaptation.
What skills are most important for the AI-driven workplace?
Skills in digital literacy, critical thinking, problem-solving, and AI tool usage are crucial.
How soon will AI impact most industries?
Many industries are already seeing AI adoption, but widespread transformation will occur over the next 5–10 years.
Can small businesses benefit from AI and automation?
Yes, cloud-based AI tools and automation platforms make advanced technology accessible to small and medium enterprises.
How does AI improve employee satisfaction?
By automating repetitive and mundane tasks, employees can focus on meaningful, engaging work, boosting morale.
Conclusion
The future of work is increasingly intertwined with artificial intelligence and automation. These technologies offer significant benefits, including improved productivity, enhanced decision-making, and increased efficiency, while also presenting challenges such as workforce reskilling and ethical considerations.
By embracing AI responsibly and fostering collaboration between humans and machines, organizations can create a more innovative, agile, and satisfying workplace. Just as How DevOps Automation Improves Software Deployment streamlines technical processes, AI and automation streamline work processes, enabling employees to focus on creativity, strategy, and growth.
The key to thriving in this AI-driven era lies in continuous learning, adaptable workflows, and a balance between technological efficiency and human ingenuity.